Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
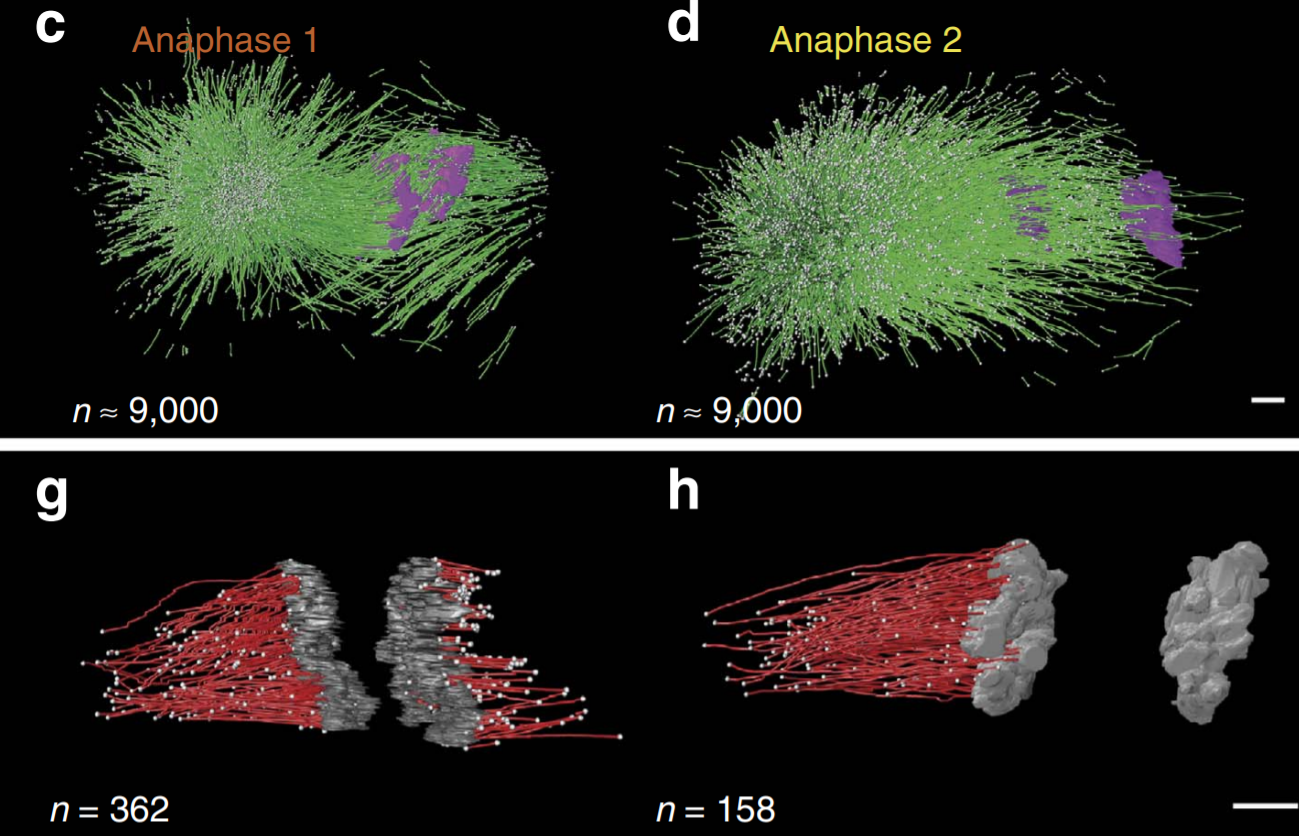
C. elegans chromosomes connect to centrosomes by anchoring into the spindle network
The mitotic spindle ensures the faithful segregation of chromosomes. Here we combine the first large-scale serial electron tomography of whole mitotic spindles in early C. elegans embryos with live-cell imaging to reconstruct all microtubules in 3D and identify their plus- and minus-ends. We classify them as kinetochore (KMTs), spindle (SMTs) or astral microtubules (AMTs) according to their positions, and quantify distinct properties of each class. While our light microscopy and muta... Read more
Stefanie Redemann, Johannes Baumgart, Norbert Lindow, Michael Shelley, Ehssan Nazockdast, Andrea Kratz, Steffen Prohaska, Jan Brugués, Sebastian Fürthauer & Thomas Müller-Reichert
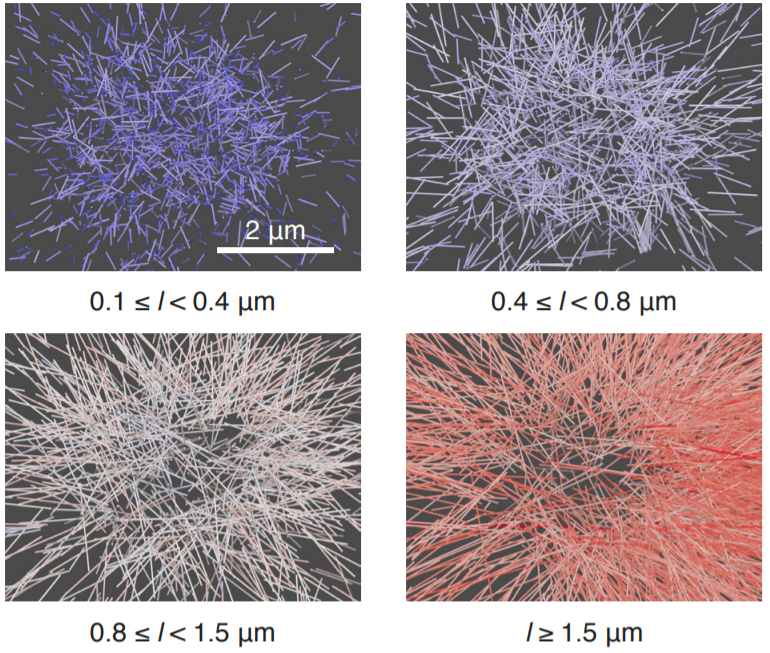
Soluble tubulin is locally enriched at mitotic centrosomes in C. elegans
During mitosis, the centrosome expands its capacity to nucleate microtubules. Understanding the mechanisms of centrosomal microtubule nucleation is, however, constrained by a lack of knowledge of the amount of soluble and polymer tubulin at mitotic centrosomes. Here we combined light microscopy and serial-section electron tomography to measure the amount of dimer and polymer at mitotic centrosomes in early C. elegans embryos. We show that a C. elegans one-cell stage centrosome at metaphase co... Read more
Johannes Baumgart, Marcel Kirchner, Stefanie Redemann, Jeffrey Woodruff, Jean-Marc Verbavatz, Frank Julicher, Anthony Hyman, Thomas Mueller-Reichert, Jan Brugues
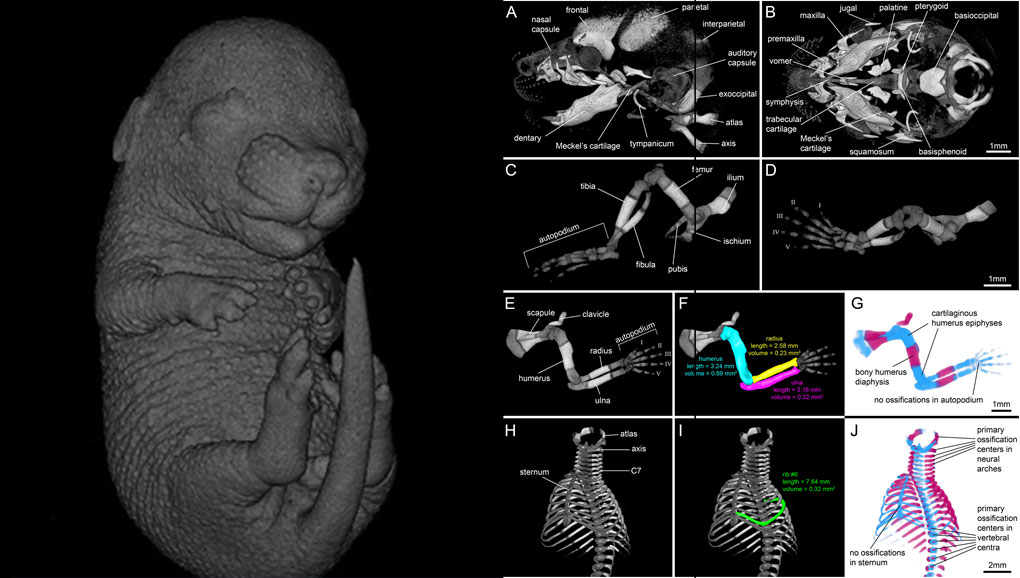
For decades, clearing and staining with Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red has been the gold standard to image vertebrate skeletal development. Here, we present an alternate approach to visualise bone and cartilage based on X-ray microCT imaging, which allows the collection of genuine 3D data of the entire developing skeleton at micron resolution.
Our novel protocol is based on ethanol fixation and staining with Ruthenium Red, and efficiently contrasts cartilage matrix, as demonstrated in wh... Read more
Simone Gabner, Peter Böck, Dieter Fink, Martin Glösmann, Stephan Handschuh
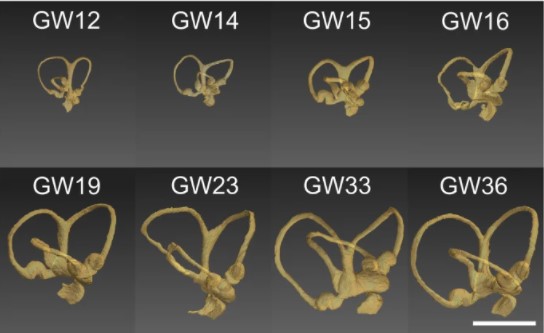
Progressive transformation of the otic placode into the functional inner ear during gestational development in humans leads to the acquisition of hearing perception via the cochlea and balance and spatial orientation via the vestibular organ.
Using a correlative approach involving micro-computerized tomography (micro-CT), transmission electron microscopy and histological techniques we were able to examine both the morphological and cellular changes associated with human inner ear devel... Read more
Lejo Johnson Chacko, David Wertjanz, Consolato Sergi, Jozsef Dudas, Natalie Fischer, Theresa Eberharter, Romed Hoermann, Rudolf Glueckert, Helga Fritsch, Helge Rask-Andersen, Anneliese Schrott-Fischer & Stephan Handschuh
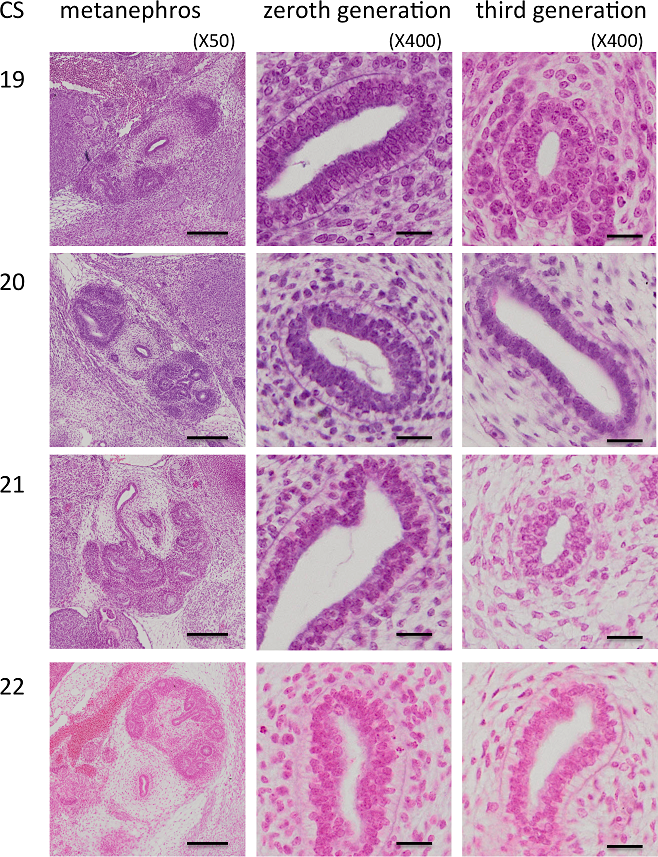
Branching morphogenesis of the urinary collecting system in the human embryonic metanephros
An elaborate system of ducts collects urine from all nephrons, and this structure is known as the urinary collecting system (UCS). This study focused on how the UCS is formed during human embryogenesis. Fifty human embryos between the Carnegie stage (CS) 14 and CS23 were selected from the Kyoto Collection at the Congenital Anomaly Research Center of Kyoto University, Japan. Metanephroses, including the UCS, were segmented on serial digital virtual histological sections. Three-dimensional imag... Read more
Hana Ishiyama, Aoi Ishikawa, Haruka Kitazawa, Sena Fujii, Jun Matsubayashi, Shigehito Yamada, Tetsuya Takakuwa
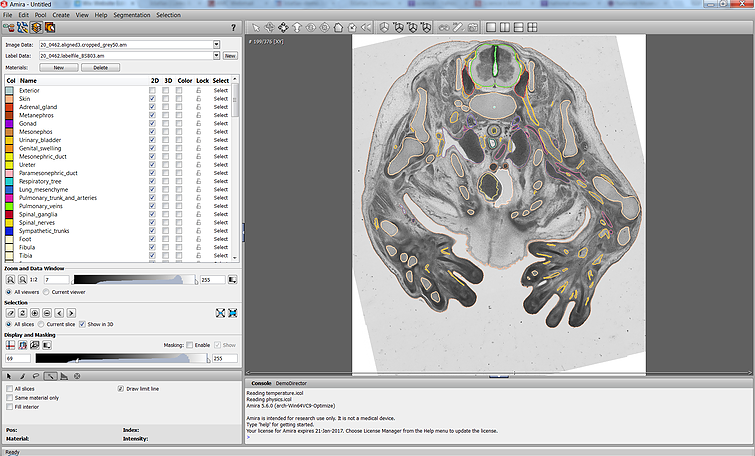
The Academic Medical Center (AMC) uses Amira to build a 3D Atlas for Human Embryology
The 3D Atlas of Human Embryology project was funded by the Academic Medical Center (AMC) in Amsterdam, the Netherlands, in 2009. Since then, over 75 students, under the supervision of embryologists of the Department of Anatomy, Embryology & Physiology, have contributed to this labor-int... Read more
Academic Medical Center